CHIFENG ZHONG, MINGZHI GAO, BINGQUAN MAO
(Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Industry , SINOPEC , 100013, China)
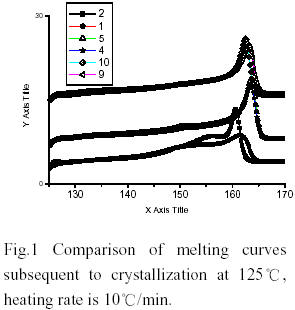
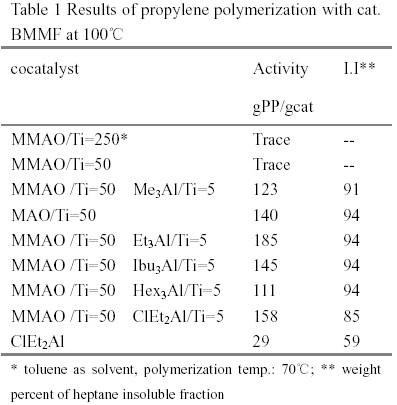
It is well known that the industrial polymerization temperature of MgCl2-supported Ziegler-Natta catalysts are around 70~80℃. Both the activity and the stereospecificity of MgCl2-supported Ziegler-Natta catalysts decease when the polymerization temperature rises over 80 ℃ [1,2]. Methylaluminoxane(MAO) is a powerful activator for group IV metallocenes in the field of olefin polymerization catalysis. Commercial MAO solutions contain a high percentage of trimethyaluminium (TMA)(30-35%). MMAO used was prepared by pumping off TMA from commercial solution. The results obtained with MMAO and alkylaluminiums in the polymerization with TiCl4/MgCl2/BMMF(9,9-bis(methoxymethyl)fluorine) at polymerization temperature 100℃ were shown in Table 1. It is worth noting that this catalyst has almost no activity with MMAO. However, additions of small quantity of alkylaluminiums (Al/Ti=5) lead to high activity and high proportions of isotactic poly(propylene)(PP). The results of DSC showed that PPs obtained with cocatalyst(MMAO and alkylaluminium) and cocatalyst(the same alkylaluminium) had the same melting point temperature and identical endothermic peaks. Additionally, the PP obtained with TMA and with MMAO and TMA both exhibited bimodal endothermic peak (Fig. 2). The average molecular wight and molecular weight distribution obtained with cocatalyst(MMAO and alkylaluminium) and cocatalyst ( the same aluminium) were almost same(Table 2). The [mmmm] pentad content of the isotactic PPs obtained with cocatalysts(MMAO and alkylaluminiums) varied with these alkylalumiums. It implied that MMAO was not an efficient activator and alkylalumiums are real activators for propylene polymerization. According to [3], the MMAO was reported as more efficient activator than crude MAO in olefin polymerization with metallocenes and TMA in crude MAO played a poisoning role.
In agreement with previous proposals [3,4,5] in metallocenes and MAO for olefin polymerization, a hypothetical structure is shown in scheme 1. Structure A is a tight ion pair which is inefficient for the activation of propylene polymerization. The addition of small amounts of alkylalumiums would disrupt the strong interaction between MAO and titanium species and form a separated ion pair (structure B) that is active for propylene polymerization.
Acknowledgement:
We thank Dr. Dongbing Liu for kindly providing MMAO.
Reference
1. S. Kojoh,M. Kioka,N. Kashiwa. Eur Polym J. 35,751-755(1999)
2. Zhong Chifeng,Gao Mingzhi,Mao Bingquan. J. App. Polym. Sci. 90,3980-3986(2003)
3. J.N. Pedeutour, H. Cramail, A. Deffieux. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 174, 81-87(2001)
4. M. Bochmann, S. J. Lancaster. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engel. 33. 1634(1994)
5. D.E. Babushkin, N.V. Semikolenova, V.A. Zakharow, E.P. Talsi. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 201 558-567(2000)



论文来源:Asia Polymer Symposium(APOSYM/2004)October 10-16