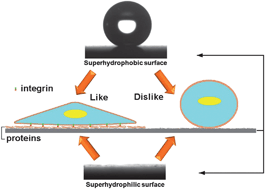
- Soft Matter, 2013, 11, 2985-2999. Interactions between cells or proteins and surfaces exhibiting extreme wettabilities
- 来源:宋文龙副教授个人网站 2015-08-25
Regulation of protein adsorption and cell adhesion on surfaces is a key aspect in the field of biomedicine and tissue engineering. Beside the general studies on hydrophilic/hydrophobic surfaces, there are both fundamental and practical interests to extend the investigation of the interaction between proteins or cells and surfaces to the two extreme wettability ranges, namely superhydrophilicity and superhydrophobicity. This review gave an overview of recent studies onproteins or cells action on these two special wettability ranges. The first part will focus on the interaction between proteins and superhydrophilic/superhydrophobic surfaces. The second part will focus on cells adhesion on these extreme wettable surfaces. Surfaces can be patterned to control in space the wettability within extreme values. As an application of such substrates, flat chips for high-throughput screening are also addressed to offer new insight on the design of a new type of bioanalysis supports.


- [来源:中国聚合物网]
- 了解更多请进入: 宋文龙副教授个人网站
- · ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(32), 17545-17551. Ultrafast Spreading Effect Induced Rapid Cells Trapping into Porous Scaffold with Superhydrophilic Surface,
- · Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 13435–13439. Adhesion switch on a Gecko-foot inspired smart nanocupule surface
- · Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 1, 1400009. Design of Multi-Stage Thermal Responsive Wettable Surface
- · Biomed. Mater. 2013, 8 045008. Bioinspired methodology for preparing magnetic responsive chitosan beads to be integrated in a tubular bioreactor for biomedical applications