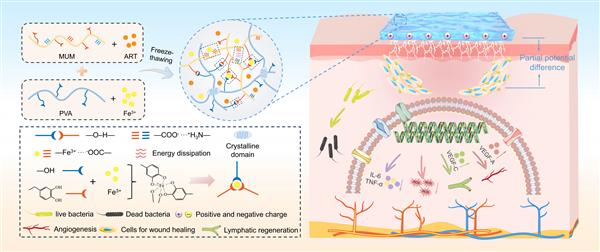
由硕士研究柴新想等完成的的研究论文“Highly adhesive, stretch, antioxidative and antibacterial double-network hydrogel containing artemisinin for?infected wound?closure and healing ”被《Chemical Engineering Journal》(IF=13.2)录用发表。
祝贺!!
Abstract: Infected wounds can trigger excessive oxidative stress and chronic inflammation, delaying wound healing, consequently placing a burden on human health and socioeconomics. In clinical applications, there is a lack of multifunctional wound dressings that combine antibacterial and antioxidant with good tension and adhesion properties. This study developed hydrogel dressings composed of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/mussel mucin (MUM)/ferric ion (PVA/MUM-Fe)/artemisinin (ART) (PVA/MUM-Fe/ART) by freeze-thawing method. The energy dissipation of PVA crystals and the double-network based on hydrogen and coordination bonds endow the hydrogel with high structural stability, strength and toughness. The hydrogel exhibited good tissue adhesion and ROS-scavenging properties due to the rich dopamine groups in the hydrogel. Furthermore, the hydrogel also exhibited good antibacterial, anti-inflammatory properties and high biocompatibility. In vivo results demonstrated that compared to commercial dressings, the resultant hydrogel dressing facilitated wound healing on an infected full-thickness skin defect by upregulating the growth factors such as VEGF-A and VEGF-C and downregulating that of inflammatory factor IL-6 and TNF-α. Transcriptomic results revealed that as-fabricated hydrogel dressing could promote the healing and regeneration of wound tissue by regulating inflammatory reaction, cell proliferation and migration, angiogenesis and matrix remodeling.
Keywords: hydrogel; wound healing; ROS-scavenging; double-network; biocompatibility