Recent advances in polymer microneedles for drug transdermal delivery: Design strategies and applications
writer:Rui Wang, Guohua Jiang,* Uladzislau E. Aharodnikau, Khaydar Yunusov, Yanfang Sun, Tianqi Liu, Sergey
keywords:Microneedle; Transdermal delivery; Manufacturing method; Biomedicine; Diabetes; Cancer
source:期刊
specific source:Macromolecular Rapid Communications
Issue time:2022年
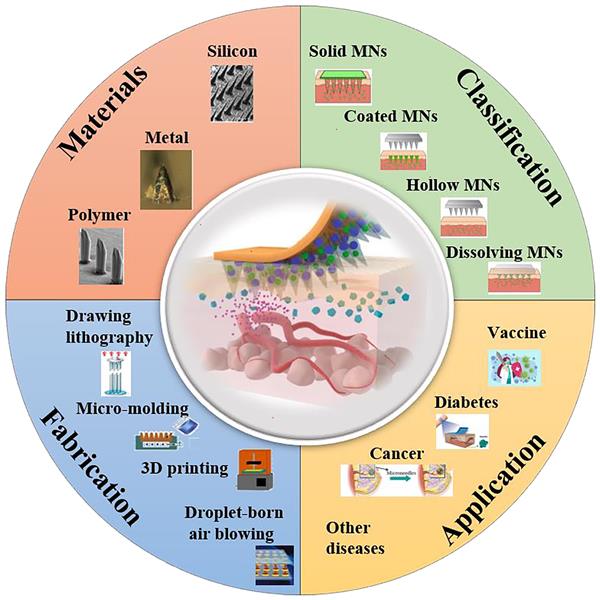
Abstract: In recent years, the transdermal drug delivery based on microneedles (MNs) technology has received extensive attention, which offers a safer and painless alternative to hypodermic needle injection. They can pierce the stratum corneum and deliver drugs to the epidermis and dermis-structures of skin, showing prominent properties such as minimally invasive, bypassing first-pass metabolism, and self-administered. A range of materials have been used to fabricate MNs, such as silicon, metal, glass, and polymers. Among them, polymer MNs have gained increasing attention from pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies as one of the promising drug delivery methods. Microneedle products have recently become available on the market, and some of them are under evaluation for efficacy and safety. This paper focuses on current state of polymer MNs in the drug transdermal delivery. The materials and methods for the fabrication of polymer MNs and their drug administration are described. The recent progresses of polymer MNs for treatment of cancer, vaccine delivery, blood glucose regulation, androgenetic alopecia, obesity, tissue healing, myocardial infarction and gout are reviewed. The challenges of MNs technology are summarized and the future development trend of MNs is also prospected.