Liposomes functionalized with cyclic RGD for targeted chemo-photothermal-combined thrombus therapy
writer:Guolong Shi, Minglin Ji, Sedrati Manar, Jing Chen*, Guohua Jiang*
keywords:thrombosis, liposome, targeting
source:期刊
specific source:Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology
Issue time:2026年
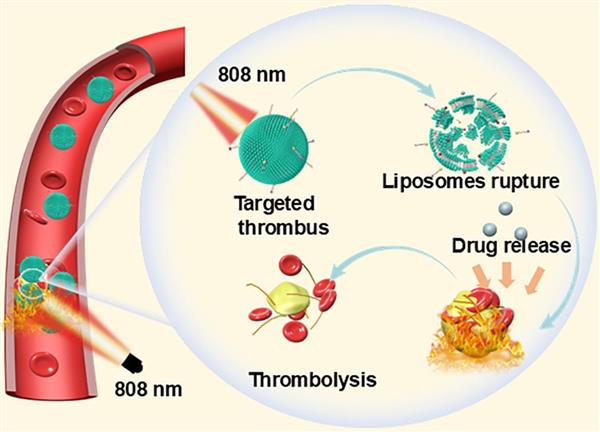
Abstract: Antithrombotic medications, including antiplatelet drugs, anticoagulants, and thrombolytics, remain fundamental to the clinical management of thrombosis, as they are widely used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and other conditions to prevent and treat thrombotic events. Thrombolytic agents, such as urokinase and streptokinase, are pivotal in the treatment of acute thrombotic diseases by activating the fibrinolytic system to dissolve blood clots. However, these agents face challenges due to their limited targeting specificity, short half-life, and varying efficiency, which can result in suboptimal therapeutic outcomes. In this study, we developed cyclic RGD (cRGD)-functionalized liposomes (IR/LK@cLip) to encapsulate IR-780 and lumbrokinase (LK). Leveraging the affinity of the RGD sequence for activated platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors, we aimed to improve the targeted chemo-photothermal combined therapy for thrombi. The cRGD can specifically target GPIIb-IIIa receptors, which are overexpressed on activated platelets, enabling the fabricated liposomes to actively recognize thrombi. When exposed to near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation, IR-780, acting as a photosensitizer, can induce the disintegration of liposomes and promote the release of LK, which enhances drug penetration efficiency by increasing thrombus porosity. In vivo studies have confirmed that IR/LK@cLip exhibits effective accumulation at the site of thrombus formation. Moreover, the IR/LK@cLip has demonstrated the ability to rapidly restore blood circulation at thrombosed locations, suggesting its potential as a powerful antithrombotic treatment.
Keywords: thrombosis, liposome, targeting