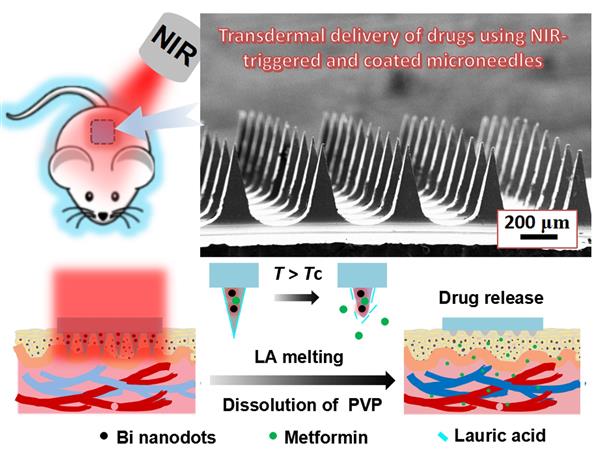
Fabrication of dissolving microneedles with thermal-responsive coating for NIR-triggered transdermal delivery of metformin on diabetic rats
作者:Depeng Liu, Yang Zhang, Guohua Jiang,* Weijiang Yu, Bin Xu,and Jiangyin Zhu
关键字:Bi nanodots, microneedles, transdermal delivery, triggered release, diabetes
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:ACS Biomaterials Science and Engineering, 2018, 4, 1687-1695.
发表时间:2018年
ABSTRACT: This study described a near-infrared (NIR) light-responsive polymer-nanodots composite microneedles (MNs) used for on-demand transdermal drug delivery. Bismuth (Bi) nanodots stabilized by poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) as photothermal conversion agent and metformin as anti-diabetic drug were introduced into the dissolving MNs that coated with lauric acid (LA). When the MNs were irradiated with NIR light, light-to-heat transduction induced by the Bi nanodots caused the LA to melt. As a result, the polymer matrix was dissolved after absorbing the interstitial fluid, and enabling the encapsulated metformin release from the MNs into skin tissue. Compared with subcutaneous injection of metformin, the administration using the Bi nanodots-induced NIR responsive MNs developed in current research exhibited a remarkable hypoglycemic effect in vivo. This work indicates that the as-fabricated Bi nanodots-induced NIR responsive and LA-coated MNs have the potential applications in diabetes treatment. Additionally, this artificial MNs also have a promising platform for delivering other therapeutic drugs.