Rapid gelation of oxidized hyaluronic acid and succinyl chitosan for integration with insulin-loaded micelles and epidermal growth factor on diabetic wound healing
作者:Jiangying Zhu, Guohua Jiang,* Wenjie Hong, et al.
关键字:rapid gelation; hydrogel; wound healing; diabetic rats; insulin; epidermal growth factor
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:Materials Science and Engineering C: Materials for Biological Applications
发表时间:2020年
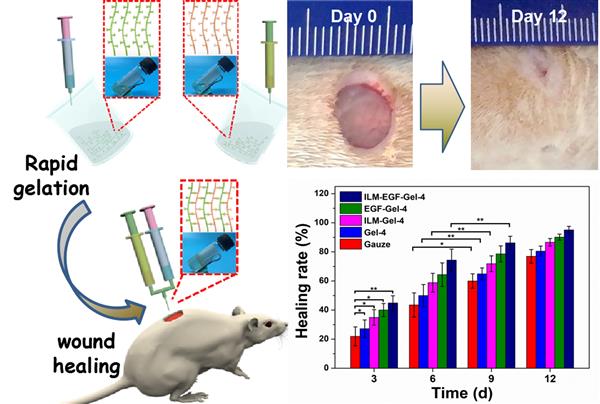
Abstract: In this work, poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly[3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid–co-styrene] (PEG-b-P(PBA-co-St) has been firstly synthesized for loading of insulin to form insulin-loaded micelles. Insulin-loaded micelles (ILM) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) are further embedded into the oxidized hyaluronic acid (OHA) and succinyl chitosan (SCS) composite hydrogels, which can be rapidly gelled by the linkage of pH-responsive C-N double bond. Then, the morphology, rheology, degradation, swelling and cytotoxicity properties of the as-prepared composite hydrogels are investigated to evaluate the biosecurity as the wound dressing. Finally, the composite hydrogels are applied to repair the wounds of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The results reveals the as-prepared composite hydrogels with ILM and EGF can promote the growth of fibroblasts and collagen deposition in diabetic rats, and accelerated the healing of wounds. Thus, the ILM- and EGF-loaded composite hydrogels have a potential in the treatment of diabetic wound healing.