Yongqiang Guo#, Genjiu Xu#, Xutong Yang, Kunpeng Ruan, Tengbo Ma, Qiuyu Zhang, Junwei Gu*, Yalan Wu*, Hu Liu and Zhanhu Guo*. Significantly Enhanced and Precisely Modeled Thermal Conductivity in Polyimide Nanocomposites by Chemically Modified Graphene via in-situ Polymerization and Electrospinning-hot press Technology. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(12): 3004-3015. 2016IF=5.256. (1区/Top期刊:工程技术领域顶尖期刊).
DOI: 10.1039/c8tc00452h
Abstract
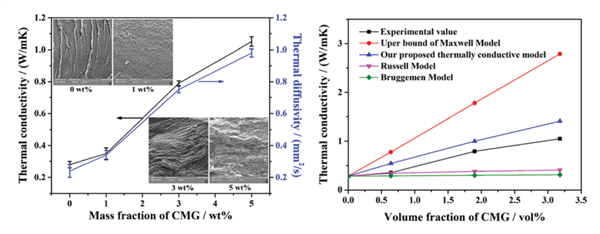
Both aminopropylisobutyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (NH2-POSS) and hydrazine monohydrate were utilized to functionalize graphene oxide (GO), and to obtain chemically modified graphene (CMG), which was then used for preparing thermally conductive CMG/polyimide (CMG/PI) nanocomposites via a sequential in situpolymerization and electrospinning-hot press technology. NH2-POSS molecules were grafted on the GO surface, and CMG was obtained by the reaction between NH2-POSS and GO. The thermal conductivity coefficient (λ), glass transition temperature (Tg) and heat resistance index (THRI) of the prepared CMG/PI nanocomposites were all increased with increasing the CMG loading. The λ value of the CMG/PI nanocomposites with 5 wt% CMG was significantly improved to 1.05 W m-1 K-1, about 4 times higher than that of the pristine PI matrix (0.28 Wm-1K-1). The corresponding Tg and THRI values were also increased to 213.0 and 282.3 °C, respectively. Moreover, an improved thermal conductivity model was proposed and predicted the λvalues of the nanocomposites more precisely than those obtained from the typical Maxwell, Russell and Bruggemen classical models.
论文链接:http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/tc/c8tc00452h/unauth#!divAbstract