课题组关于两亲性分子二次组装的研究发表在Chem. Eur. J.上
Ultrasound-Driven Secondary Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic β-Cyclodextrin Dimers
Hai-tao Zhang, Xiao-dong Fan,* Wei Tian,* Rong-tian Suo, Zhen Yang, Yang Bai, and Wan-bin Zhang
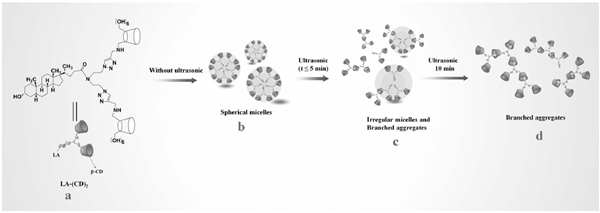
The controlled secondary self-assembly of amphiphilic molecules in solution is theoretically and practically significant in amphiphilic molecular applications. An amphiphilic β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) dimer, namely LA-(CD)2, has been synthesized, wherein one lithocholic acid (LA) unit is hydrophobic and two β-CD units are hydrophilic. In an aqueous solution at room temperature, LA-(CD)2 self-assembles into spherical micelles without ultrasonication. The primary micelles dissociates and then secondarily form self-assemblies with branched structures under ultrasonication. The branched aggregates revert to primary micelles at high temperature. The ultrasound-driven secondary self-assembly is confirmed by transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, 1H NMR spectroscopy, and Cu2+-responsive experiments. Furthermore, 2D NOESY NMR and UV/Vis spectroscopy results indicate that the formation of the primary micelles is driven by hydrophilic–hydrophobic interactions, whereas host–guest interactions promote the formation of the secondary assemblies. Additionally, ultrasonication is shown to be able to effectively destroy the primary hydrophilic–hydrophobic balances while enhancing the host–guest interaction between the LA and β-CD moieties at room temperature.
全文链接:http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/chem.201405707/abstract