Viscoelastic Behavior and Model Simulations of Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Biocomposites with Carbon Nanotubes: Hierarchical Structures and Relaxation
writer:Kunshan Ding, Nengxin Wei, Yanan Zhou, Yi Wang, Defeng Wu, Haiyun Liu, Hai Yu, Chao Zhou, Jianxiang
keywords:poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate); carbon nanotubes; composite; creep; melt rheology.
source:期刊
specific source:Journal of Composite Materials
Issue time:2016年
Journal of Composite Materials 2016, 50(13), 1805-1816
ABSTRACT:
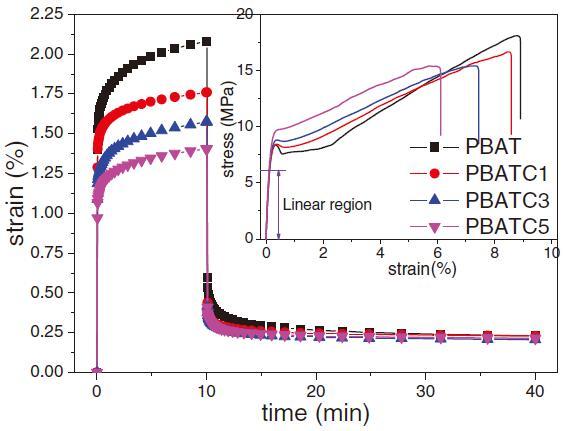
Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) biocomposites containing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were prepared by melt compounding. The linear viscoelasticity of composites, including creep, creep-recovery and stress relaxation in the solid state, and dynamic shear flow in the molten state, were studied and then further described by the viscoelastic models, aiming at exploring relaxation of hierarchical structures of CNTs and obtaining structural parameters of CNTs in PBAT matrix. The results reveal that CNTs are dispersed mainly as flocs or small aggregates in PBAT, which is further confirmed by the structural parameters of CNTs obtained through model simulations on the dynamic rheological responses of composites. The presence of CNTs retards overall kinetics of creep and stress relaxation of PBAT. This is attributed to highly restrained viscoelastic and viscoplastic deformation of PBAT chain coils, rather than slightly confined elastic deformation of chain segments because the chain coils is in the same size-scale with the CNT flocs.
PDF DOWNLOAD:
http://jcm.sagepub.com/content/50/13/1805