Constructing Reversible Phases through Solvent Engineering towards Activating Asynchronous Shape Morphing and Sensing Capability of Biodegradable Polyesters
作者:Chenguang Jiang, Jing Song, Yuchen Chao, Jiali Jiao, Defeng Wu*
关键字:polyester thermoset; reversible phase; shape-memory programming.
论文来源:期刊
具体来源:Polymer
发表时间:2026年
Polymer, 2026, 346, 129660.
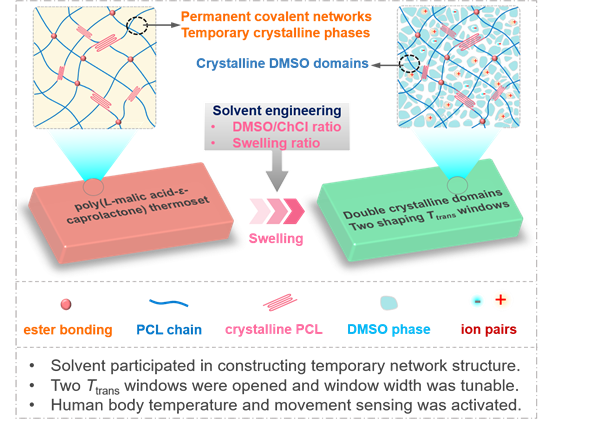
Constructing multiple reversible domains is vital for diversifying shape shifting path of shape memory polymer (SMP). Herein, we proposed a solvent-engineering strategy to build the second temporary phase in the dually cross-linked polyester. Poly(L-malic acid-ε-caprolactone) (P(MA-CL)) was synthesized via the esterification of 3-arm PCL and L-malic acid oligomers. Two characteristic crosslinks, covalent ester-bonding and crystalline PCL phase domains, were formed in this polyester thermoset. After being swollen by dimethyl sulfoxide/choline chloride (DMSO/ChCl) solvents, an additional temporary phase, the crystalline DMSO domain, was introduced. The phase transition temperatures of the two crystalline domains differed significantly, and could be tuned easily by altering the swelling ratio of thermoset and DMSO/ChCl ratio. This opened two shape shifting temperature windows, therefore activating asynchronous morphing capability of thermoset. Moreover, the existence of co-solvent ChCl gave the thermal sensing capability to the swollen thermoset, and desirable sensitivity occurred around the phase change temperature of DMSO. Thus, the strategy proposed here is effective for building multiple actuation-controlling units in the polyester thermoset based SMP, in this way to manufacture polyester-based intelligent device with integrated actuating and sensing capabilities.
PDF DOWNLOAD:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032386126001072