聚对苯撑苯并二噁唑(PBO)纤维被誉为21世纪的超级纤维,其衍生的PBO纳米纤维(PNF)被视为制备高性能透波复合纸的理想原材料,在航空/航天、交通运输和5G通讯等领域具有广阔的应用前景。然而,PNF透波复合纸内的纳米纤维间的相互作用力较低,且PNF表面疏水性较差使其难以服役暴雨、冰雪、盐雾等恶劣自然环境。
西北工业大学化学与化工学院顾军渭教授“结构/功能高分子复合材料”(SFPC)课题组团队基于铁离子(Fe3+)与PNF表面N原子的配位作用在PNF间构建金属配位键获得预成型的三维互联纳米纤维网络,并通过溶胶-凝胶-薄膜转化法制备PNF纸;再在PNF纸表面喷涂聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)颗粒/P(S-co-BCB-co-MMA)混合溶液,经热交联制备双层结构PTFE-P/PNF纳米复合纸。
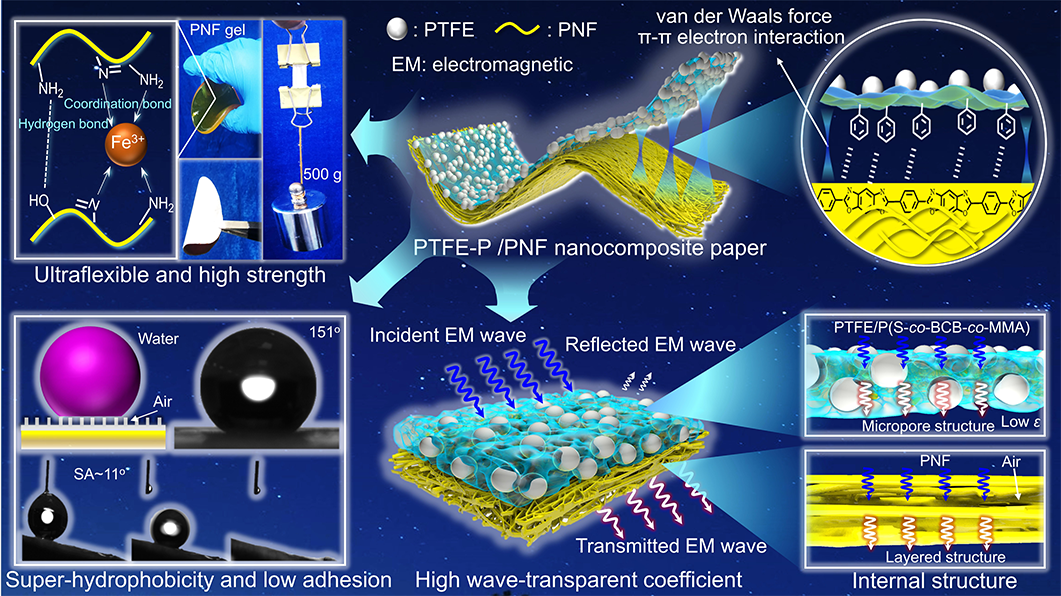
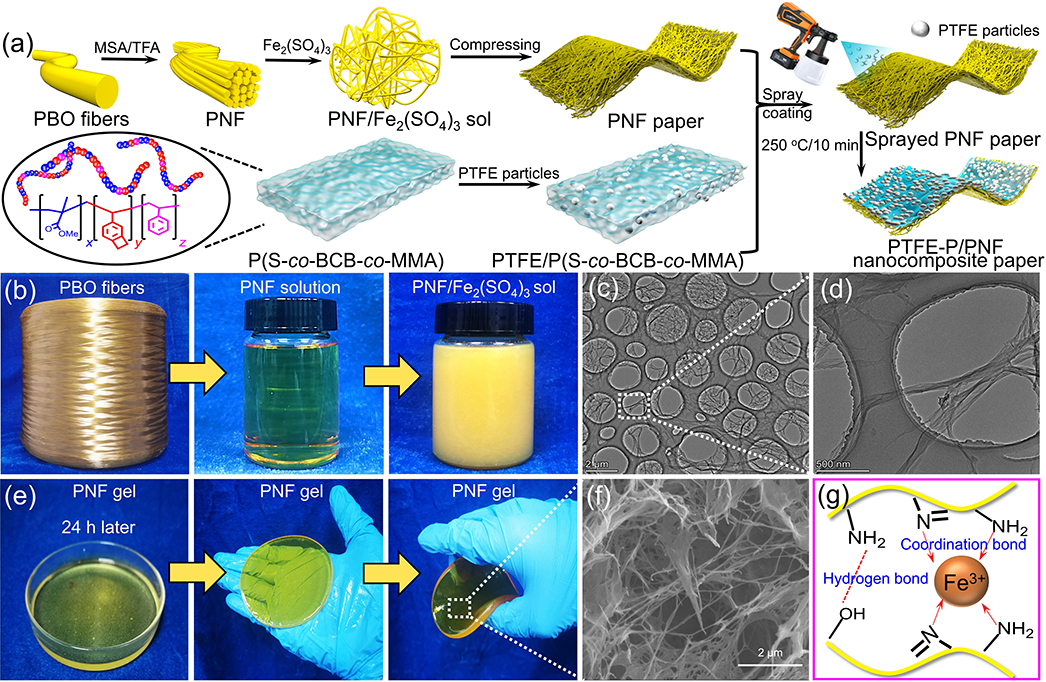

Fig. 3. Morphology of PNF, P/PNF and PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite paper. Optical photographs of PNF (a), P/PNF (d), and PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite (e) paper; SEM images of PNF (b), P/PNF (e), and PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite (h) paper; SEM images of fracture surfaces for PNF (c), P/PNF (f), and PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite (i) paper.
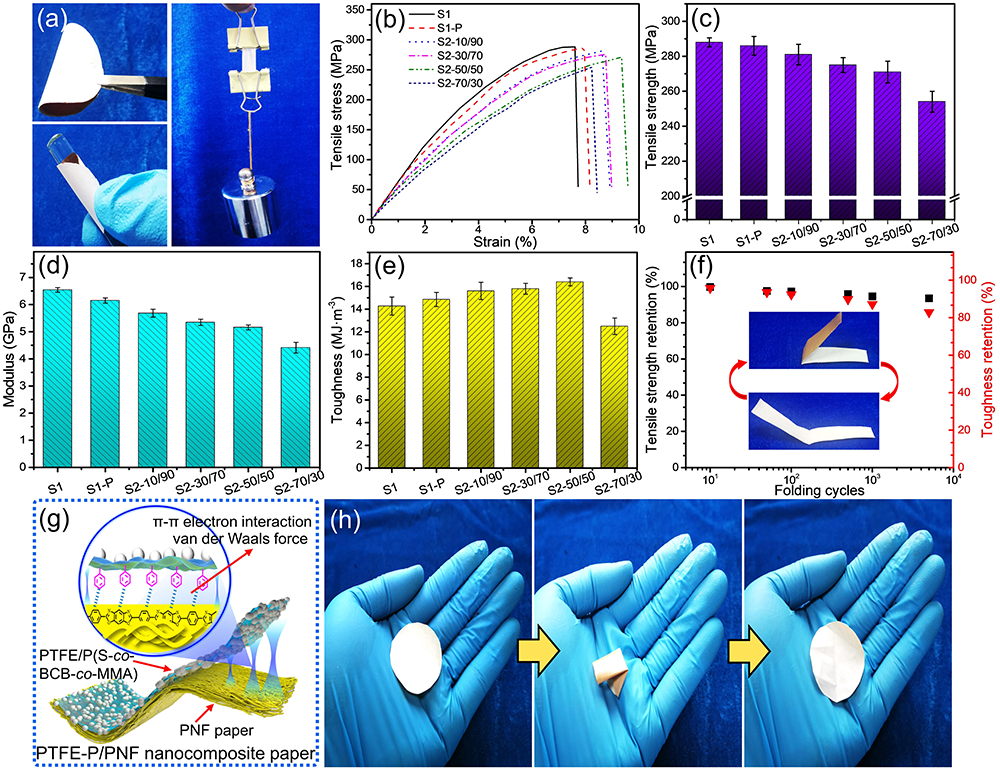
Fig. 4. Mechanical properties and folding resistance of PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite paper. Optical photographs of the PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite paper possessing ultraflexibility and withstanding a weight of 500 g (a); tensile stress-strain curves (b), tensile strength (c), modulus (d), and toughness (e) of the PNF, P/PNF and PTFE-P/PNF nanocomposite paper; tensile strength and toughness retention of the PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite paper after repetitive folding (f); schematic diagram of the mechanism of interactions between the PTFE/P(S-co-BCB-co-MMA) and the PNF paper for fabricating the PTFE-P/PNF nanocomposite paper (g); optical photographs of the PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite paper being continuously folded and unfolded, showing no breakage (h).

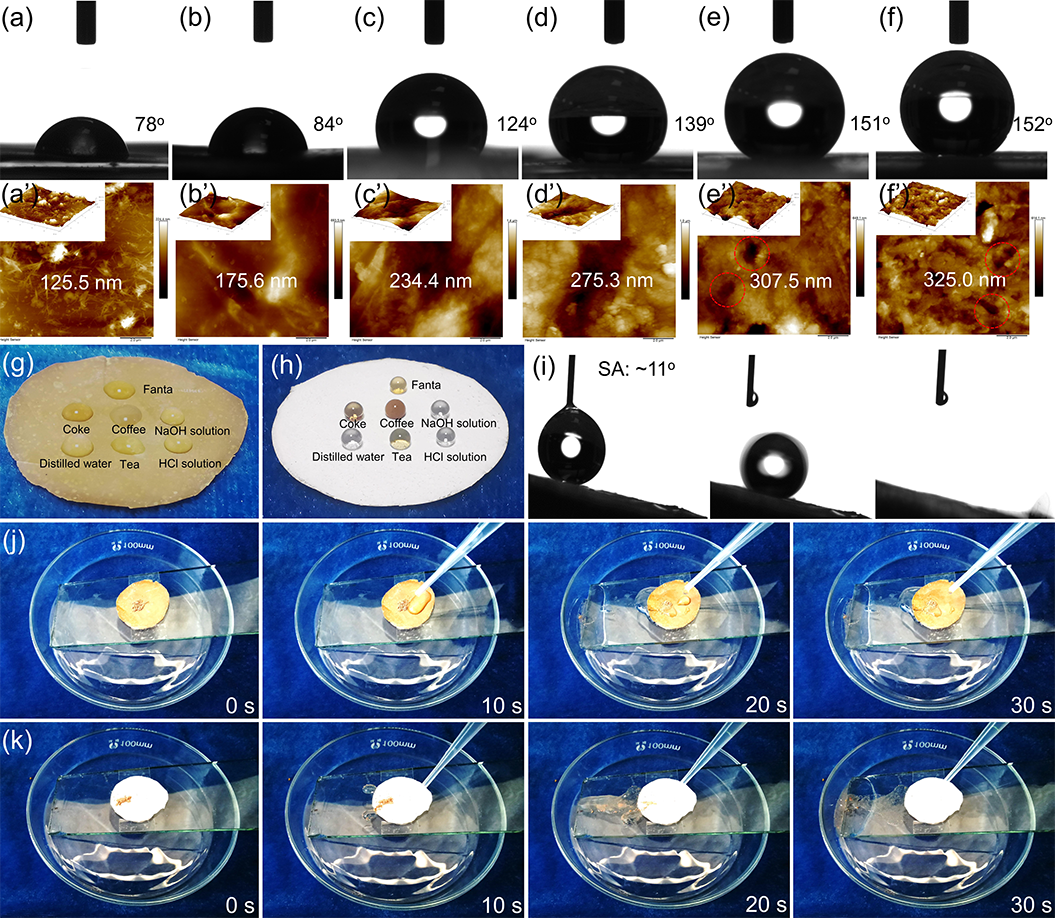
Fig. 6. Hydrophobicity and self-cleaning properties of PTFE-P/PNF nanocomposite paper. Contact angles and AFM images of distilled water with PNF (a, a’), P/PNF (b, b’), and PTFE-P/PNF nanocomposite (c-f, c’-f’) paper; optical photographs of different liquids on the surface of the PNF paper (g) and PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite paper (h); representative contact process of a water droplet (5 μL) on the surface of the PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite paper with a sliding angle of about 11o (i); self-cleaning process of the PNF paper (j), and the PTFE-P/PNF-50/50 nanocomposite paper (k) with dust as a mode of contaminant.
论文信息:Lin Tang, Yusheng Tang, Junliang Zhang, Yuhan Lin, Jie Kong, Kun Zhou* and Junwei Gu*. High-strength super-hydrophobic double-layered PBO nanofiber-polytetrafluoroethylene nanocomposite paper for high-performance wave-transparent applications. Science Bulletin, 2022, 10.1016/j.scib.2022.10.011.
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2022.10.011
作者简介:

顾军渭,西北工业大学化学与化工学院教授、博导,陕西省杰出青年科学基金获得者、第四届中国复合材料学会青年科学家奖获得者。当选英国皇家化学会Fellow,英国皇家航空学会Fellow;入选科睿唯安全球“高被引科学家”、爱思唯尔“中国高被引学者”。任陕西省高分子科学与技术重点实验室副主任、中国复合材料学会导热复合材料专业委员会常务副主任。主要从事功能高分子复合材料和纤维增强先进树脂基复合材料的设计制备及加工研究。获2021年度中国复合材料学会科学技术奖二等奖(1/8)、2020年度高等学校科学研究优秀成果奖(科学技术)技术发明二等奖(2/6),2021中国化学会高分子创新论文奖等。主持国家自然科学基金联合基金重点项目,XXX技术基础重点项目、陕西省杰出青年科学基金等省部级及以上项目20项。以第一和/或通讯作者在Adv Funct Mater, Angew Chem Int Edit, Compos Sci Technol和Macromolecules等期刊发表高水平SCI论文150余篇。4篇论文入选2018~2020年“中国百篇最具影响国际学术论文” 、1篇论文入选第七届中国科协优秀科技论文、1篇论文入选“领跑者5000-中国精品科技期刊顶尖学术论文”。主/参编Elsevier、Wiley出版社专著4部,授权中国/美国发明专利20余件。任Nano-Micro Lett、J Mater Sci Technol、Compos Sci Technol、Natl Sci Rev等期刊副主编或编委。
- 北理工化工学院在锂电池高安全性隔膜研究领域取得新进展 2016-04-26
- 北京化工大学岳冬梅教授团队 AFM:兼具卓越室温自修复、可回收与极端温度力学稳定性的高强度聚脲弹性体 2025-12-11
- 吉林大学孙俊奇教授课题组 NSR:基于强韧且可变形的纳米相区制备超高强度和超高韧性的可逆交联塑料 2025-11-22
- 华南理工王小慧/雷泽芃教授 ACS Nano:兼具高强度、优异阻燃性、耐溶剂性和可化学回收的热加工型纤维素网络聚合物 2025-10-20
- 湖北大学张玉红/陈朝霞、湖北工程学院刘勇Compos. Part B:具有光热转换、抗菌、耐久性超疏水海绵用于油水分离和原油回收 2025-09-30
- 天津大学潘莉教授团队 CEJ:多功能氟化环烯烃聚合物 - 高效合成、性能精准调控及其在光学与超疏水表面的前沿应用 2025-09-22
- 青岛大学明津法团队 IJBM:兼具超疏水和光热效应的聚乳酸纤维气凝胶用于防冰除冰功能开发 2025-08-17
