
先进锂金属电池的开发是满足高能量密度和高效率储能系统需求的一种有前途的方法。但是液态电解液的低安全性、界面不稳定性和高反应性极大地阻碍了锂金属电池的发展。准固态电解质(QGPEs)具有优良的力学性能和高相容性,可以满足LMBs的需求。然而,大多数聚合物基体的机械强度较低,难以抵抗枝晶的穿透。而衍生的准固态GPEs与电极的物理化学相容性较差,导致电池容量衰减甚至短路。
基于此,中南大学潘安强教授团队在国际知名期刊Advanced Functional Materials上发表题为“Regulation of Interphase Layer by Flexible Quasi-Solid Block Polymer Electrolyte to Achieve Highly Stable Lithium Metal Batteries”的研究论文。
本文要点
要点一:基于原位缩聚和物理共混制备了嵌段结构PALE聚合物基体
首先,利用聚乳酸中的-COOH基团和EG中的-OH基团原位共聚,合成了具有三嵌段分子链结构的PLLA-EG-PLLA前驱体(PLE)。这种嵌段结构可以有效提高聚合物链的稳定性,并引入更多的电负性官能团。然后,将PLE前驱体与PAN共混并通过静电纺丝工艺制备三维PALE复合膜,并将其用作GPEs基体。XRD、FT-IR、1H NMR等结果证明PLE嵌段结构和PAN与PLE分子间相互作用,SEM结果证明聚合物基体的多孔隙结构。这种嵌段结构显著提高了聚合物基体的柔韧性,而且聚合物基体表现出优异的LEs吸收性和阻燃性。
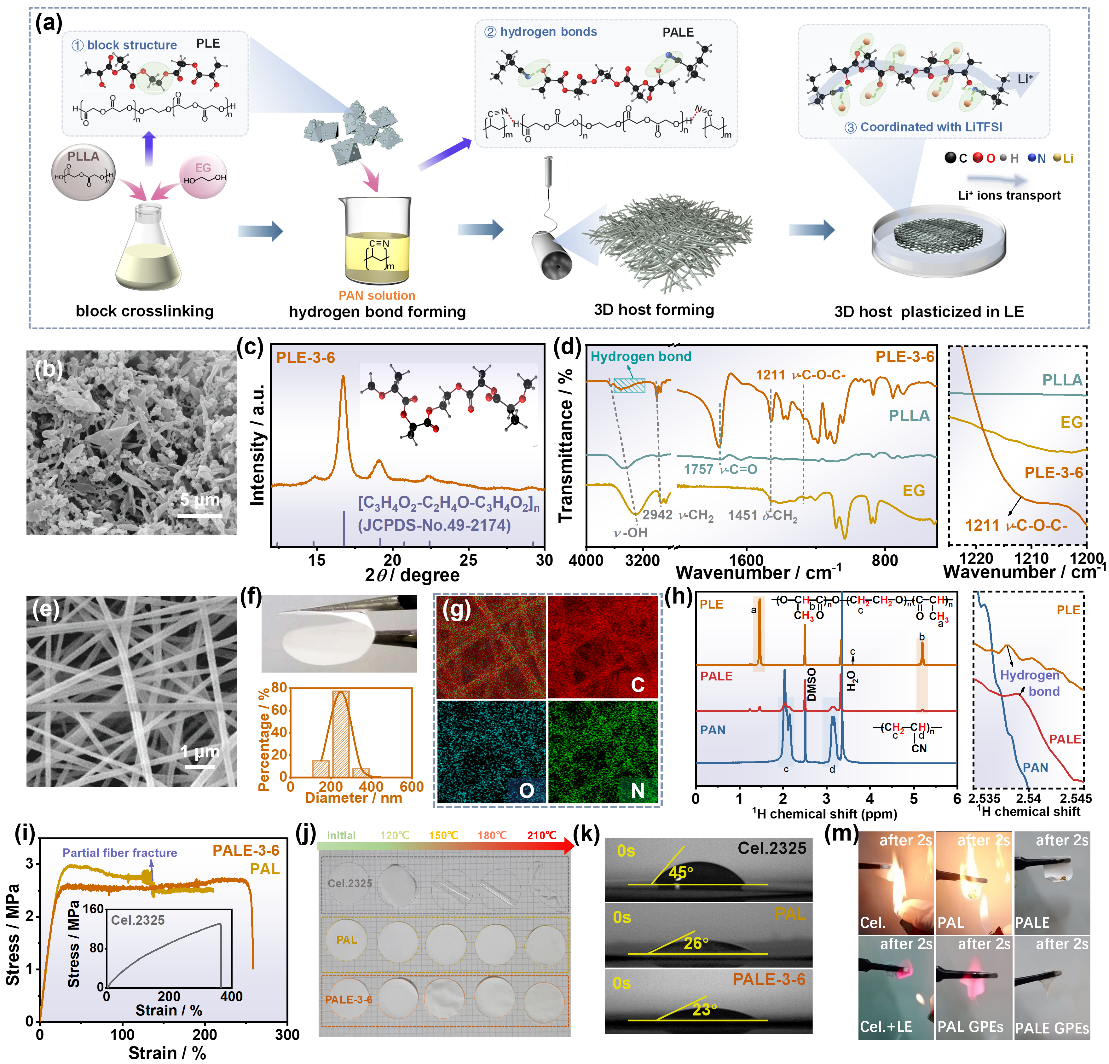
Figure 1. (a) Schematic diagram of the synthesis process of the block PLE precursor powders and the 3D PALE GPEs. (b) FE-SEM images (c) XRD pattern, and (d) FT-IR spectra of PLE-3-6 copolymer precursor, right: partial enlarged detail in 1200-1230 cm-1. (e) FE-SEM image, (f) flexibility and diameter distribution, corresponding (g) EDS mapping, and (h) 1H NMR of PALE-3-6 membrane host, left: in range of 0-6 ppm, right: partial enlarged detail in 2.535-2.545 ppm. (i) The stress-strain curves, (j) the thermal shrinkage, and (k) electrolyte affinity test of membrane skeletons of Cel.2325, PAL and PALE-3-6 membranes. (m) Combustion tests of membrane skeletons and electrolytes.
要点二:PALE GPEs抑制枝晶生长并形成有机/无机界面层
研究了PALE GPEs与锂金属的兼容性及界面形貌演化。Li||PALE GPEs||Li和Cu||PALE GPEs||Li在不同面电流密度和面容量条件下表现出优异的循环稳定性,表明PALE GPEs与锂金属电极良好的相容性。同时,具有丰富极性亲锂基团的PALE聚合物链对Li盐的强锚定作用及聚合物链的缠连结构使电解质可以缓冲电极的体积变化,诱导Li+离子沿聚合物链均匀转移。电池循环后的锂金属表面致密光滑,表明PALE GPEs可以有效抑制锂枝晶生长,同时,在锂金属电极上形成了由有机/无机沉积组成的薄而致密的SEI层。
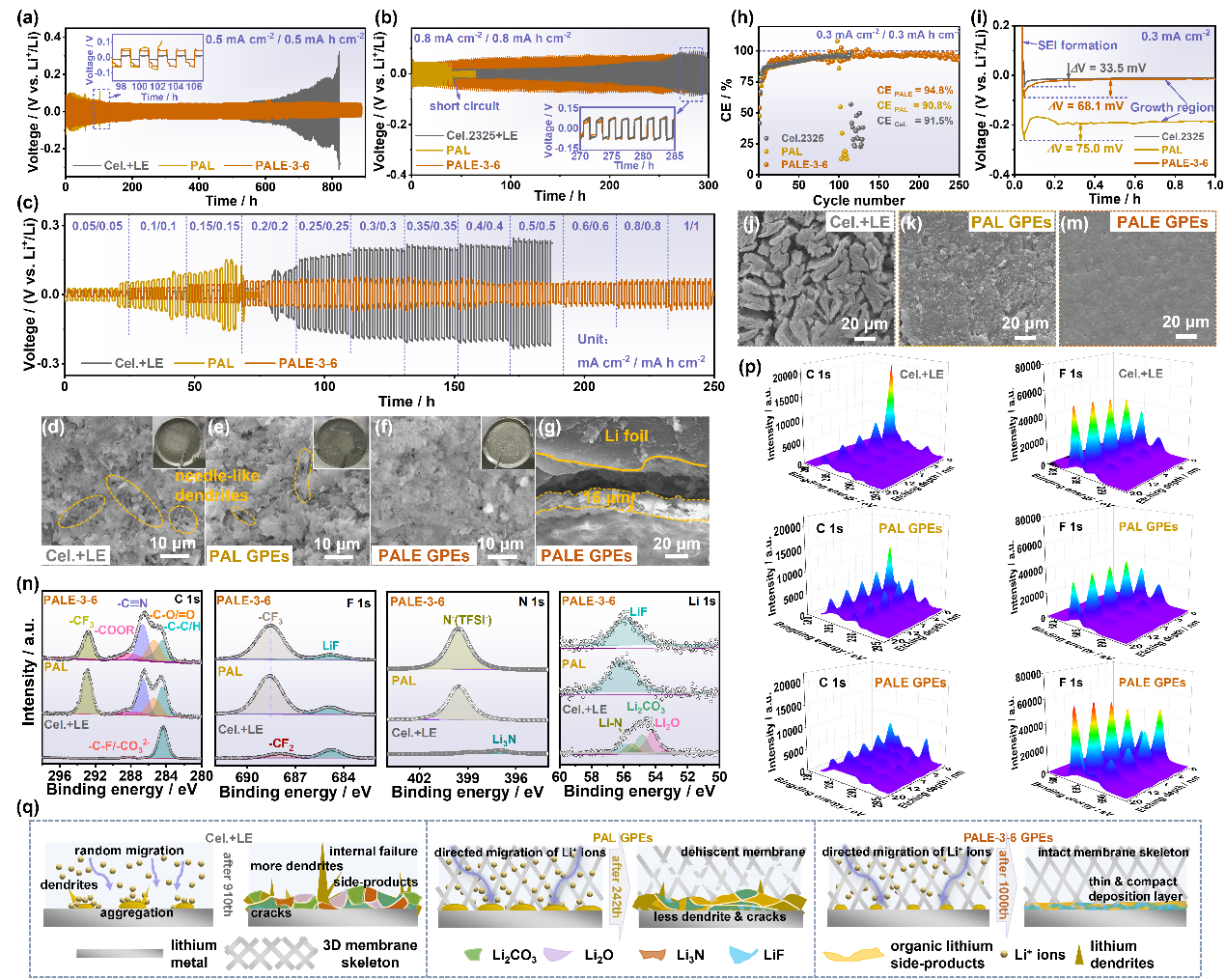
Figure 2. Voltage profiles of Li plating/stripping in symmetric Li cells with different electrolytes under test conditions of (a) 0.5 mA cm-2/0.5 mA h cm-2 and (b) 0.8 mA cm-2/0.8 mA h cm-2. (c) Voltage profiles of Li||Li symmetric cells at step-increased current densities. SEM images of cycled Li anodes disassembled from (d) LE, (e) PAL and (f) PALE-3-6 GPEs after plating/stripping at 0.3 mA cm-2/0.3 mA h cm-2. (g) Cross-sectional SEM of Li anode from cycled PALE-3-6 GPEs-based battery. (h) Coulombic efficiencies and (i) voltage profiles of Li plating/stripping in Li||Cu battery at 0.3 mA cm-2/0.3 mA h cm-2. SEM images of Li deposited layer on Cu foils in Li||Cu battery based on (j) LE, (k) PAL and (m) PALE-3-6 GPEs after long-term cycling. (n) XPS spectra of C 1s, F 1s, N 1s and Li 1s of cycled Li anodes from Li||Li symmetric batteries (0.3 mA cm-2/0.3 mA h cm-2). (p) XPS depth profiles of cycled Li anodes from Li||Li symmetric batteries with different electrolytes after 50 h at 0.5 mA cm-2. (q) The deposition mechanism of Li+ ions and the schematic diagram of Li anode surface in batteries assembled with LE, PAL and PALE-3-6 GPEs.
要点三:PALE GPEs抑制正极氧化腐蚀
同时,利用SEM、TEM、ICP-OES和XPS验证了PALE GPEs与正极活性的界面兼容性,结果表明,循环后的正极活性颗粒表面生成了均匀无机LiF和有机锂盐的CEI层,不仅有利于离子传输,而且可以有效避免电极开裂及活性颗粒粉化。因此,基于PALE GPEs的全电池在高活性物质负载或面电流测试条件下均表现出优异的循环稳定性。
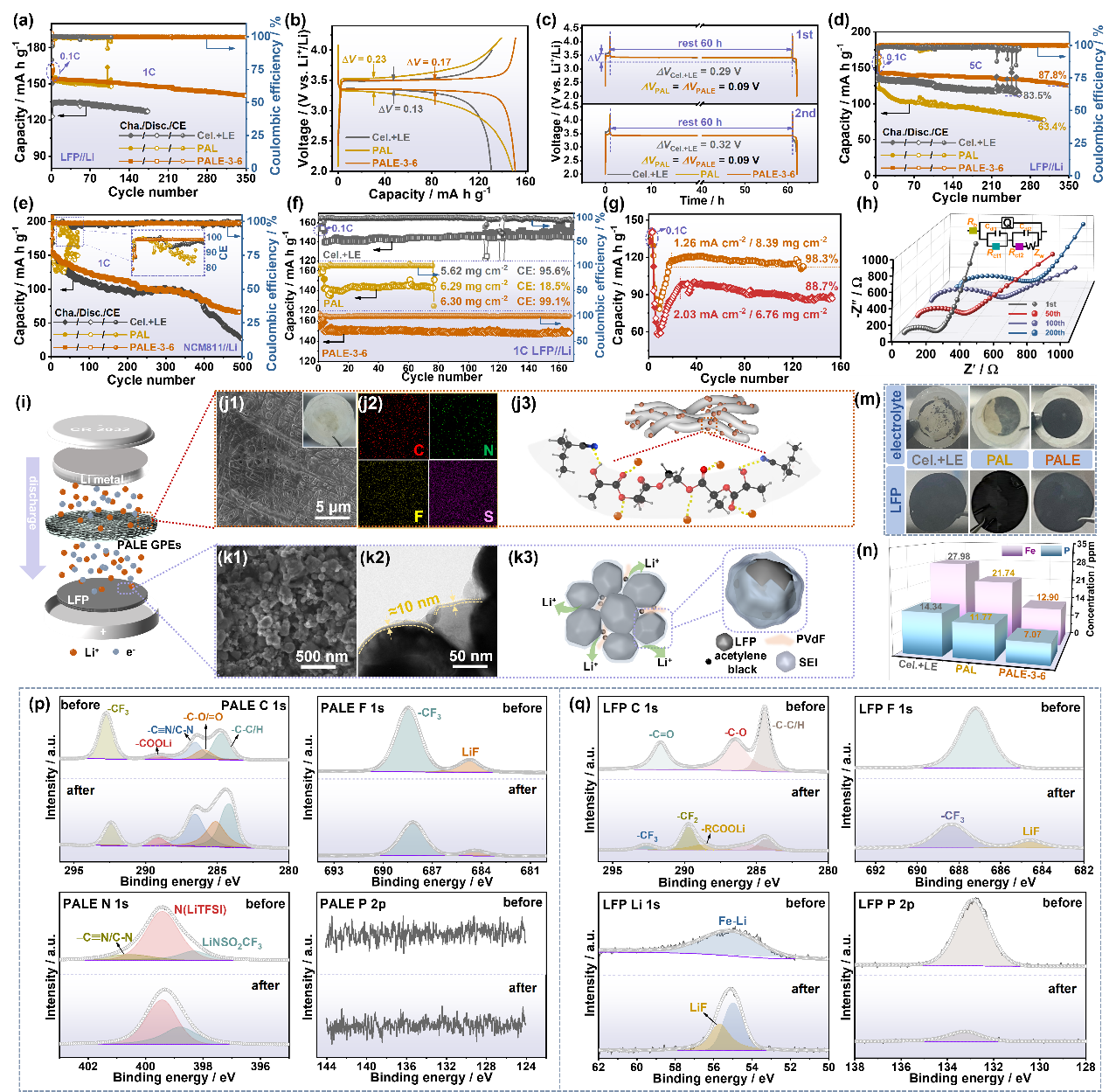
Figure 3. (a) Long-term cycling performances and (b) the 100th charge/discharge potential-plateau curves of LFP||Li batteries using LE, PAL and PALE-3-6 GPEs at 1C. (c) Self-discharge charge/discharge curves of LFP||Li batteries at 1C. Long-term cycling performances of (d) LFP||Li batteries at 5C and (e) NCM811||Li batteries at 1C. Cycling performance of batteries based on (f) high LFP loading and different electrolytes at 1C, and (g) high current densities of high LFP loading with PALE GPEs. (h) EIS spectra of LFP||PALE-3-6||Li battery at different cycles. (i) Structure schematic diagram of coin-cell based on PALE-3-6 GPEs. (j1) SEM images (Inset e: optical photograph) and (j2) EDS mapping of PALE-3-6 GPEs from cycled LFP||Li battery at 1C. (j3) Diagram of Li+ ion migration in PALE-3-6 GPEs during cycling. (k1) SEM, (k2) TEM images and (k3) illustration of CEI layer formed on cycled LFP particle in LFP||PALE||Li battery. (m) Optical photographs of membrane skeletons and LFP electrodes with high loading. (n) ICP-OES of dissolution concentrations of Fe and P ions in high loading LFP cathode. The XPS spectra of the (p) PALE-3-6 GPEs and (q) LFP electrodes before and after cycling.
要点四:PALE GPEs在柔性软包电池中具有实用性
鉴于PALE GPEs在扣式电池中优异的电化学和力学性能,研究了其在锂金属软包电池中的实用性。负极为厚度为450 μm或46.4 μm的锂金属,正极为面载量为2-5 mg cm-2的LFP。LFP||PALE GPEs||Li软包电池不仅具有优异的容量保持率和库伦效率,而且在正常、折叠、卷曲和切割状态下都能点亮LED灯带,没有出现发生明显的光源亮度变化,表明了PALE GPEs在高能量密度柔性电池中的应用可能性。

Figure 4. (a) Structure illustration of pouch cells and (b) the actual size of LFP electrode. (c) Cycling performance, (d) charge/discharge profiles at different cycles and (e) median voltage of the flexible LMB using PALE-3-6 GPEs at 1C and 2C. (f) Cycling performance the PALE-3-6 GPEs-based pouch cell assembled with lithium metal anode (< 50 μm) and LFP cathode (4.4 mg cm-2) at 0.5C. (g) Optical photograph for flexible PALE LMB that powered LED strip at different states.
文章第一作者是中南大学柴思敏,通讯作者是潘安强教授和常智教授。
文章链接
Regulation of Interphase Layer by Flexible Quasi-Solid Block Polymer Electrolyte to Achieve Highly Stable Lithium Metal Batteries
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202300425
通讯作者简介
潘安强教授简介:中南大学材料科学与工程学院教授,材料物理系主任。先后入选了教育部新世纪优秀人才,湖湘青年英才,湖南省“芙蓉学者奖励计划”青年学者,教育部“长江学者奖励计划”青年学者,湖南省科技创新领军人才。主要研究领域为二次动力与储能电池。迄今为止在Nat. Commun.,Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Adv. Mater., Adv. Energy Mater., Adv. Funct. Mater., Energy Environ. Sci., Nano Energy., Energy Storage Mater.等国际知名期刊上发表论文150余篇,其中IF>10论文40余篇,论文引用10000余次。申请发明专利20余项,参加国内外会议并作邀请报告20余次,论文引用7000余次。
Email: pananqiang@csu.edu.cn
常智教授简介:中南大学材料科学与工程学院教授,博士生/硕士生导师,2022年入选国家海外高层次青年人才项目(海外优青)。主要从事高比能锂离子电池/锂金属电池电解液,功能性隔膜,固态电解质,金属负极保护等方向的研究。近五年发表SCI论文60余篇,其中以第一作者(含共同)/共同通讯作者在Joule,Nat. Commun.,Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,Adv. Mater.,Energy Environ. Sci.,Adv. Funct. Mater.,Energy Storage Mater.,Small,J. Mater. Chem. A等刊物上发表论文26篇,他引超过3700次,H因子31,申请国家发明专利6项。担任SCI期刊Materials客座编辑,eScience期刊青年编委以及Nat. Commun.,Adv. Mater.,Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,Energy Environ. Sci.,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,Adv. Funct. Mater.,Adv. Energy Mater.,Energy Storage Mater.等著名国际期刊的审稿人。
Email: zhichang@csu.edu.cn
- 宁波材料所陈涛/肖鹏团队《Adv. Mater.》: 柔性凝胶电子器件实现吸湿-解吸实时监测与智能化湿度管理 2026-02-05
- 广西大学王睿猛 、赵祯霞团队 AFM:压缩触发动态氢键LDH@纤维素半柔性微纳气凝胶瞬时释放纳米塑料用于可持续水修复 2026-01-31
- 澳门大学姜颖课题组诚招博士后、博士生、研究助理 - 柔性器件方向(高分子材料/电子/生物医学工程等) 2026-01-24
- 东华大学廖耀祖/吕伟课题组、西安交通大学王嘉楠教授 AFM: 咪唑基离子化COF纳米纤维骨架构建快充准固态锂金属电池 2025-09-14
- 北化周伟东教授团队 Nat. Commun.: 新型准固态聚合物电解质助力高电压锂金属电池实现非破坏性寿命延长 2025-04-21
- 四川大学王玉忠院士团队陈思翀教授/吴刚教授 Adv. Sci.:多尺度耦合复合准固态电解质助力火安全长寿命锂金属电池 2025-03-28
- 上海交大梁正/颜徐州/岳昕阳 JACS:一种变革性的分子肌肉固态电解质 2025-12-22
