材料表界面改性及功能化是开发材料用途,特别是开发航空航天、新能源、生物医药等高附加值应用的一个关键环节。然而鉴于材料种类多样性所造成的表面化学性质和物理结构的巨大差异,研究和发展同时满足基材普适性、方法简单温和性以及功能可控多样性这三大特征的表界面改性技术具有巨大的挑战性。
针对上述问题,陕西师范大学化学化工学院杨鹏教授课题组对天然大分子介导的材料表界面功能化进行了系统深入的研究,首次发现解折叠溶菌酶分子在气-液、固-液界面自组装形成的宏观二维纳米薄膜。值得强调的是,该薄膜内部具有丰富的类淀粉样蛋白聚集体结构,而淀粉样蛋白结构实际上代表了自然界除贻贝足丝蛋白之外的另一大类生物粘合体系。受生物体借助淀粉样结构稳定粘附的启发,溶菌酶纳米薄膜实现了快速、温和、稳定的表面粘附,是一种可大面积制备的多功能仿生纳米界面材料。基于此,该工作创制出了区别于聚多巴胺体系的表面功能化新策略,克服了聚多巴胺体系改性层显色、涂层稳定差等缺点。

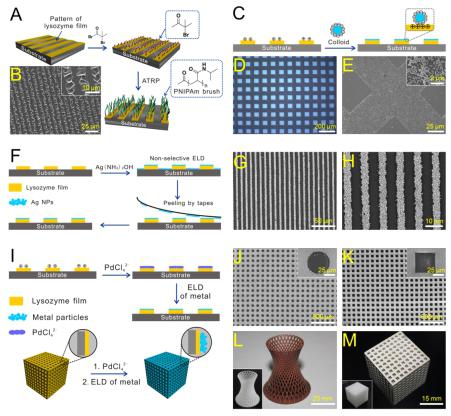
此外,可通过紫外曝光或电子束直写,实现溶菌酶薄膜微/纳米级的图案化。利用化学刻蚀可将自身图案转移至SiO2、Au和Cu等衬底表面,摆脱了传统光刻胶旋涂、烘焙等繁琐步骤,是一种易大规模制备且绿色环保的正性光刻胶。该工作还利用薄膜表面丰富的反应性基团,成功地合成出了图案化的聚合物刷;又借助溶菌酶表面的正电位,基于薄膜在普适性基材表面的稳定吸附以及易于高分辨率图案化等特点,实现了胶体纳米颗粒的图案化化自组装以及Cu、Ag的选择性无电沉积。基于溶菌酶纳米薄膜自上而下和自下而上的微/纳米制造技术,不仅克服了传统方法操作繁琐、不利于图案化、普适性低等缺点,还提高了制备过程的环境友好性,为材料表面的微/纳米制造提供了一种新的途径。
杨鹏课题组组建于2012年底,主要致力于蛋白质类淀粉样组装的多功能仿生界面材料及其在表界面功能化中的应用研究。经过几年的努力,已取得了较为丰富的研究成果,已在Macromol. Biosci. (2012, 12, 1053)、Chem. Comm. (2012, 48, 8787)、Chem. Rev. (2013, 113, 5547)、ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. (2014, 6, 3759)、Adv. Mater. Interfaces (2015, 2, 1400401)、Soft Matter (2015, 11, 3094)、Adv. Mater. (2016, 28, 579, VIP paper) 等权威学术期刊发表综述和研究论文十余篇。
摘要快递:
2D Protein Supramolecular Nanofilm with Exceptionally Large Area and Emergent Functions
Advanced Materials
DOI: 10.1002/adma.201506476
Published: 23 Jun 2016
The development of ersatile materials and engineering devices requires multifunctional conformal coatings that gains increasing interests. However, few methods can achieve a stable, large-area and colorless coating on substrates with different structure, composition and shapes. We report the one-step aqueous coating of virtually arbitrary material surfaces using self-assembled macroscopic bionanofilm made by pure lysozyme. The unfolding and subsequent phase transition of commercially available lysozyme initiates the spontaneous formation of 2D amyloid-like nanofilm at a vapor/liquid or liquid/solid interface with a macro-scale size (e.g. 20 inches in diagonal) and shape in a few minutes. The attachment of the nanofilm onto various surfaces could be accordingly achieved by the amyloid-mediated adhesion, and the robust adhesion stability supports the nanofilm to safely pass the adhesive tape peeling test. The nanofilm coating displays competitive advantages over existing alternatives including controlled thickness from nano to micro-scale, colorless and optical transparency, stable bonding strength, ordered internal and surface morphology, as well as thermal/chemical stability. Multifunctions on the nanofilm coating have been demonstrated through great implications in both top-down and bottom-up micro/nano-scale interfacial engineering including surface modification, all-water-based photo/electron beam-lithography and electroless deposition. This finding deciphers an unbeknown interfacial assembly function for proteins that is useful to achieve a 2D biological material with the properties being useful in practical implications.
链接: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/wol1/doi/10.1002/adma.201506476/abstract
- 提出“表面能匹配”界面设计法则 - 福建物构所林悦/宁波材料所林正得 AFM:超低热阻导热界面材料研究新进展 2026-02-05
- 江苏海洋大学李成杰团队 ACS AMI:可重加工自修复的橡胶基导热界面材料用于热管理 2025-07-20
- 西工大顾军渭/阮坤鹏团队 Angew:本征高导热液晶聚二甲基硅氧烷热界面材料 2025-01-22
- 浙江大学毛峥伟教授课题组Adv. Mater.:一种通用的聚电解质-锁定策略:从普通蛋白质到稳定的展开蛋白基粘合剂以实现快速稳健的组织密封 2025-12-25
- UCLA贺曦敏/燕山大学秦志辉、焦体峰 Adv. Mater.: 具有优异机械性能和耐久性的完全可降解蛋白质凝胶-氢键供体的调控 2025-06-27
- 华东理工刘润辉教授课题组 CCS Chem.:有效稳定蛋白质的伴侣样活性丝胶蛋白 2025-06-17
- 中国科学院大学杨晗课题组诚聘博士后、副研究员 - 化学、高分子、功能材料、纳米材料等 2024-10-15
